以 b 为底数的对数是一个指数,表示我们需要将底数 b 提升多少次方才能得到该数。
当 b 的 y 次方等于 x 时:
b y = x
那么以 b 为底 x 的对数等于 y:
logb(x) = y
例如:
24 = 16
那么
log2(16) = 4
对数函数,
y = logb(x)
是指数函数的反函数,
x = by
So if we calculate the exponential function of the logarithm of x (x>0),
f (f -1(x)) = blogb(x) = x
Or if we calculate the logarithm of the exponential function of x,
f -1(f (x)) = logb(bx) = x
自然对数是以e为底的对数:
ln(x) = loge(x)
When e constant is the number:
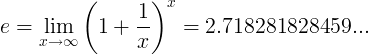
or
![]()
See: 自然对数
The inverse logarithm (or anti logarithm) is calculated by raising the base b to the logarithm y:
x = log-1(y) = b y
对数函数的基本形式为:
f (x) = logb(x)
| Rule name | Rule |
|---|---|
对数乘积法则 |
logb(x ∙ y) = logb(x) + logb(y) |
对数除法法则 |
logb(x / y) = logb(x) - logb(y) |
对数幂法则 |
logb(x y) = y ∙ logb(x) |
对数换底法则 |
logb(c) = 1 / logc(b) |
对数换底公式 |
logb(x) = logc(x) / logc(b) |
对数导数 |
f (x) = logb(x) ⇒ f ' (x) = 1 / ( x ln(b) ) |
对数积分 |
∫ logb(x) dx = x ∙ ( logb(x) - 1 / ln(b) ) + C |
负数的对数 |
当 x≤ 0 时,logb(x) 未定义 |
0的对数 |
logb(0) 未定义 |
1的对数 |
logb(1) = 0 |
底数的对数 |
logb(b) = 1 |
无穷大对数 |
lim logb(x) = ∞, 当 x→∞ |
查看: 对数规则
The logarithm of the multiplication of x and y is the sum of logarithm of x and logarithm of y.
logb(x ∙ y) = logb(x) + logb(y)
For example:
log10(3 ∙ 7) = log10(3) + log10(7)
The logarithm of the division of x and y is the difference of logarithm of x and logarithm of y.
logb(x / y) = logb(x) - logb(y)
For example:
log10(3 / 7) = log10(3) - log10(7)
The logarithm of x raised to the power of y is y times the logarithm of x.
logb(x y) = y ∙ logb(x)
For example:
log10(28) = 8∙ log10(2)
The base b logarithm of c is 1 divided by the base c logarithm of b.
logb(c) = 1 / logc(b)
For example:
log2(8) = 1 / log8(2)
The base b logarithm of x is base c logarithm of x divided by the base c logarithm of b.
logb(x) = logc(x) / logc(b)
For example, in order to calculate log2(8) in calculator, we need to change the base to 10:
log2(8) = log10(8) / log10(2)
See: log base change rule
The base b real logarithm of x when x<=0 is undefined when x is negative or equal to zero:
logb(x) is undefined when x ≤ 0
The base b logarithm of zero is undefined:
logb(0) is undefined
The limit of the base b logarithm of x, when x approaches zero, is minus infinity:
![]()
See: log of zero
The base b logarithm of one is zero:
logb(1) = 0
For example, teh base two logarithm of one is zero:
log2(1) = 0
See: log of one
The limit of the base b logarithm of x, when x approaches infinity, is equal to infinity:
lim logb(x) = ∞, when x→∞
See: log of infinity
The base b logarithm of b is one:
logb(b) = 1
For example, the base two logarithm of two is one:
log2(2) = 1
When
f (x) = logb(x)
Then the derivative of f(x):
f ' (x) = 1 / ( x ln(b) )
See: log derivative
The integral of logarithm of x:
∫ logb(x) dx = x ∙ ( logb(x) - 1 / ln(b) ) + C
For example:
∫ log2(x) dx = x ∙ ( log2(x) - 1 / ln(2) ) + C
log2(x) ≈ n + (x/2n - 1) ,
For complex number z:
z = reiθ = x + iy
The complex logarithm will be (n = ...-2,-1,0,1,2,...):
Log z = ln(r) + i(θ+2nπ) = ln(√(x2+y2)) + i·arctan(y/x))
Find x for
log2(x) + log2(x-3) = 2
Using the product rule:
log2(x∙(x-3)) = 2
Changing the logarithm form according to the logarithm definition:
x∙(x-3) = 22
Or
x2-3x-4 = 0
Solving the quadratic equation:
x1,2 = [3±√(9+16) ] / 2 = [3±5] / 2 = 4,-1
Since the logarithm is not defined for negative numbers, the answer is:
x = 4
Find x for
log3(x+2) - log3(x) = 2
Using the quotient rule:
log3((x+2) / x) = 2
Changing the logarithm form according to the logarithm definition:
(x+2)/x = 32
Or
x+2 = 9x
Or
8x = 2
Or
x = 0.25
log(x) is not defined for real non positive values of x:
| x | log10x | log2x | logex |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | undefined | undefined | undefined |
| 0+ | - ∞ | - ∞ | - ∞ |
| 0.0001 | -4 | -13.287712 | -9.210340 |
| 0.001 | -3 | -9.965784 | -6.907755 |
| 0.01 | -2 | -6.643856 | -4.605170 |
| 0.1 | -1 | -3.321928 | -2.302585 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.301030 | 1 | 0.693147 |
| 3 | 0.477121 | 1.584963 | 1.098612 |
| 4 | 0.602060 | 2 | 1.386294 |
| 5 | 0.698970 | 2.321928 | 1.609438 |
| 6 | 0.778151 | 2.584963 | 1.791759 |
| 7 | 0.845098 | 2.807355 | 1.945910 |
| 8 | 0.903090 | 3 | 2.079442 |
| 9 | 0.954243 | 3.169925 | 2.197225 |
| 10 | 1 | 3.321928 | 2.302585 |
| 20 | 1.301030 | 4.321928 | 2.995732 |
| 30 | 1.477121 | 4.906891 | 3.401197 |
| 40 | 1.602060 | 5.321928 | 3.688879 |
| 50 | 1.698970 | 5.643856 | 3.912023 |
| 60 | 1.778151 | 5.906991 | 4.094345 |
| 70 | 1.845098 | 6.129283 | 4.248495 |
| 80 | 1.903090 | 6.321928 | 4.382027 |
| 90 | 1.954243 | 6.491853 | 4.499810 |
| 100 | 2 | 6.643856 | 4.605170 |
| 200 | 2.301030 | 7.643856 | 5.298317 |
| 300 | 2.477121 | 8.228819 | 5.703782 |
| 400 | 2.602060 | 8.643856 | 5.991465 |
| 500 | 2.698970 | 8.965784 | 6.214608 |
| 600 | 2.778151 | 9.228819 | 6.396930 |
| 700 | 2.845098 | 9.451211 | 6.551080 |
| 800 | 2.903090 | 9.643856 | 6.684612 |
| 900 | 2.954243 | 9.813781 | 6.802395 |
| 1000 | 3 | 9.965784 | 6.907755 |
| 10000 | 4 | 13.287712 | 9.210340 |