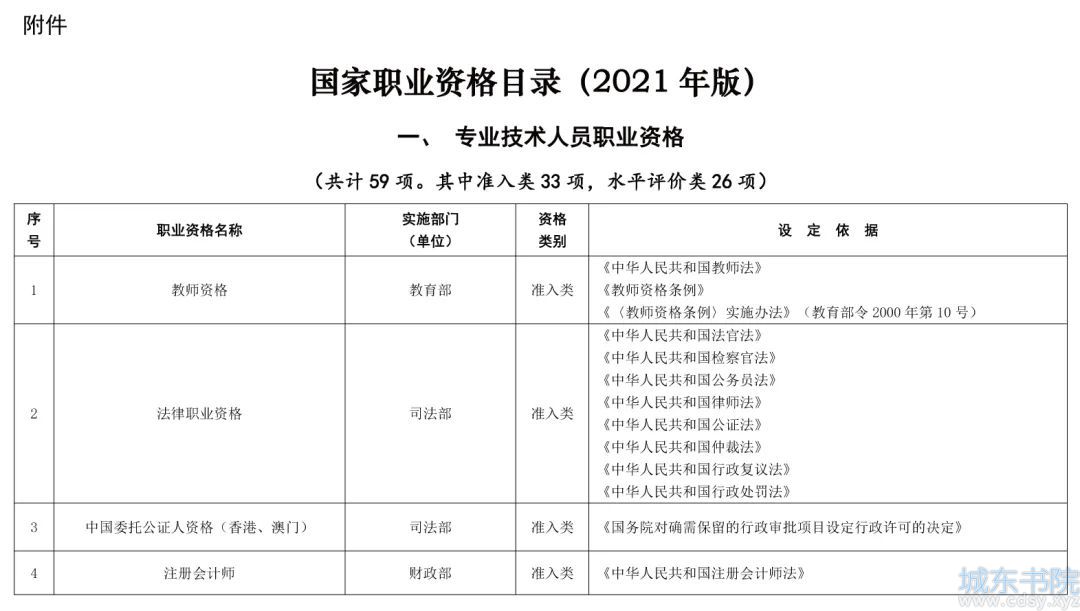
scrollTop等元素距离
关于scrollTop,offsetTop,scrollLeft,offsetLeft用法介绍
页可见区域宽: document.body.clientWidth;
网页可见区域高: document.body.clientHeight;
网页可见区域宽: document.body.offsetWidth (包括边线的宽);
网页可见区域高: document.body.offsetHeight (包括边线的宽);
网页正文全文宽: document.body.scrollWidth;
网页正文全文高: document.body.scrollHeight;
网页被卷去的高: document.body.scrollTop;
网页被卷去的左: document.body.scrollLeft;
网页正文部分上: window.screenTop;
网页正文部分左: window.screenLeft;
屏幕分辨率的高: window.screen.height;
屏幕分辨率的宽: window.screen.width;
屏幕可用工作区高度: window.screen.availHeight;

offsetTop, offsetLeft:只读属性。要确定的这两个属性的值,首先得确定元素的offsetParent。offsetParent指的是距该元素最近的position不为static的祖先元素,如果没有则指向body元素。确定了offsetParent,offsetLeft指的是元素左侧偏移offsetParent的距离,同理offsetTop指的是上侧偏移的距离。
offsetHeight, offsetWidth:只读属性。这两个属性返回的是元素的高度或宽度,包括元素的边框、内边距和滚动条。返回值是一个经过四舍五入的整数。如下图:

scrollHeight, scrollWidth:只读属性。返回元素内容的整体尺寸,包括元素看不见的部分(需要滚动才能看见的)。返回值包括padding,但不包括margin和border。如下图:

scrollTop, scrollLeft:图中已经表示的很明白了。如果元素不能被滚动,则为0。
window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight:只读。视口(viewport)的尺寸,包含滚动条
clientHeight, clientWidth:包括padding,但不包括border, margin和滚动条。如下图

Element.getBoundingClientRect():只读,返回浮点值。这个方法非常有用,常用于确定元素相对于视口的位置。该方法会返回一个DOMRect对象,包含left, top, width, height, bottom, right六个属性:
left, right, top, bottom:都是元素(不包括margin)相对于视口的原点(视口的上边界和左边界)的距离。
height, width:元素的整体尺寸,包括被滚动隐藏的部分;padding和border参与计算。另外,heigth=bottom-top, width=right-left。
jQuery常用监听页面滚动
当前滚动的地方的窗口顶端到整个页面顶端的距离:
var winPos = $(window).scrollTop();
获取指定元素的页面位置
$(val).offset().top;
对页面滚动条滚动的监听:要放在页面加载的时候
$(window).scroll(function(event){});
设置滚动条到指定位置
$(window).scrollTop(offset)






 湘公网安备 43102202000103号
湘公网安备 43102202000103号