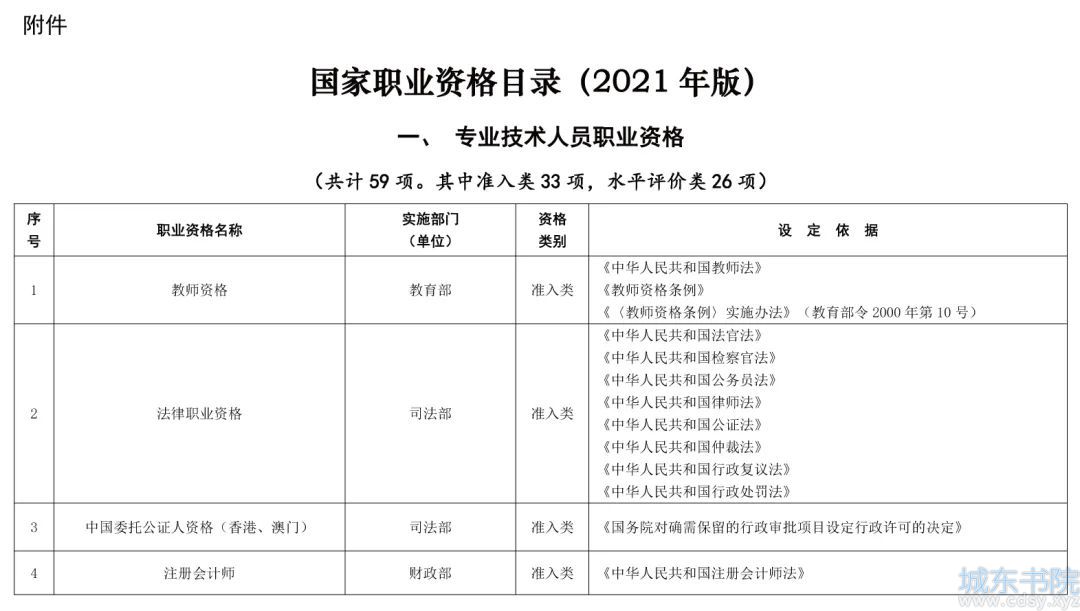
第 204 题:如何实现元素的水平垂直居中?
时间:12-14来源:作者:点击数:
在 HTML 中分为块级元素和内联元素,两者实现居中的方法都 一样,并且块级元素中还要区分定宽高和不定宽高的情况
水平居中
行内元素水平居中
父元素设置 text-align: center
<div class="container">
<p>我是内联元素</p>
</div>
<style>
.container{
width: 100%;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
/* 父元素是块级元素,直接设置text-align属性 */
text-align: center;
}
</style>
块级元素水平居中(定宽)
通过设置要居中元素的外边距来实现:margin: 0 auto
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.father {
background-color: red;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
}
.son {
background-color: sandybrown;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
/* 块级定宽,margin: 0 auto; */
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
块级元素水平居中(不定宽)
子元素设置display: inline,父元素设置text-aling: center(在设置了display: inline后会将该元素显示为行内元素,而inline不能设置宽高和上下外边距,但是可以左右外边距)
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">1111111</div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.father {
background-color: red;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
text-align: center;
}
.son {
display: inlines;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
使用定位属性实现,父元素设置 position: relative;,子元素设置 position: absolute;、left: 50%;、margin-left: -元素宽度一半
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.father {
background-color: red;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
position: relative;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
position: absolute;
background-color: blue;
left: 50%;
/* 自己宽度的一半 */
margin-left: -50px;
}
</style>
使用 flex 布局实现水平居中在父元素设置 display: flex;、justify-content: center;
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
<style>
.father {
background-color: red;
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: blue;
}
</style>
垂直居中
行内元素垂直居中
设置子元素的行高即可实现,若行内元素文本出现换行则需要给父元素添加 display: table-cell;、vertical-align: middle;
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="container">
<p>单行行内元素</p>
</div>
<!--CSS-->
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
<!-- 行内元素换行时添加display: table-cell; vertical-align: middle; -->
}
.container p{
line-height: 200px;
}
</style>
块级元素垂直居中(定高)
定宽时,使用定位实现垂直居中。父元素设置 position: relative;,子元素设置 display:absolute;、left: 50%;、margin-top: -一半高度
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="container">
<div></div>
</div>
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
position: relative;
}
.container div{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -25px;
}
</style>
块级元素垂直居中(不定高)
需要使用到 transform: translateY(-50%);
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="container">
<div>不定高度</div>
</div>
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
position: relative;
}
.container div{
width: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}
</style>
使用 flex 实现垂直居中
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="container">
<div>不定高度</div>
</div>
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.container div{
width: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
}
</style>
水平垂直居中
利用定位实现水平垂直居中,父元素设置 position: relative;,子元素设置 position: absolute;
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="container">
<div></div>
</div>
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
position: relative;
}
.container div{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
利用 flexbox 实现水平垂直居中,父元素设置 position: relative;,子元素设置 position: absolute;
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="container">
<div></div>
</div>
<!-- CSS -->
<style>
.container{
width: 500px;
height: 200px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.container div{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rosybrown;
}
</style>方便获取更多学习、工作、生活信息请关注本站微信公众号







 湘公网安备 43102202000103号
湘公网安备 43102202000103号