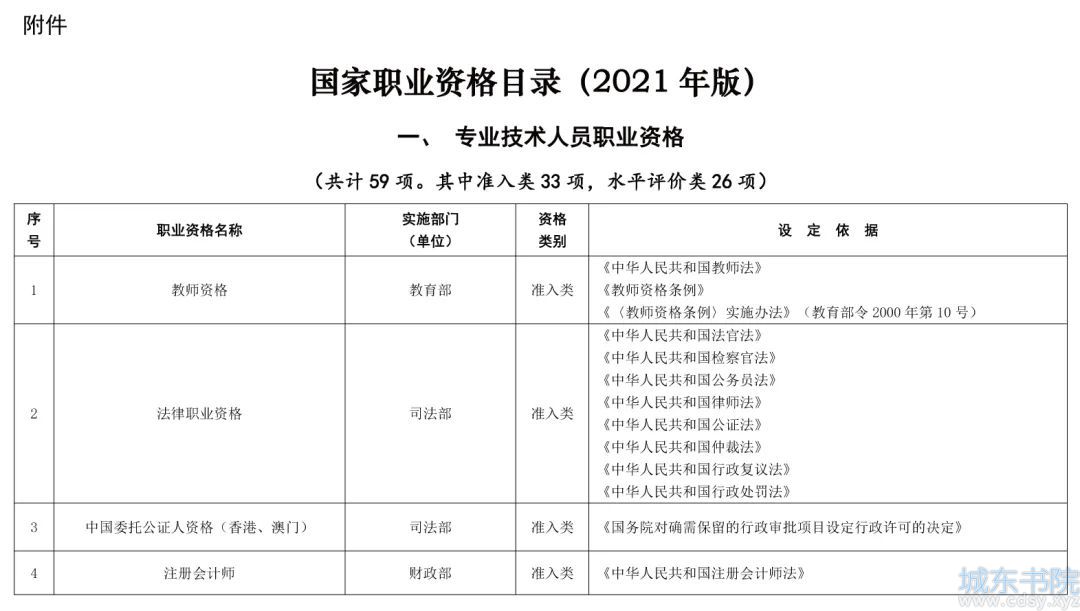
Java 线程基础
时间:12-14来源:作者:点击数:
1.无返回值的线程
继承Thread方式创建线程
public static void main(String[] arg){
new extendsThread().start();
}
static class extendsThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run()
{
System.out.println("begin execute");
try{Thread.sleep(5000);}catch (Exception e){}
System.out.println("end ");
}
}
实现 Runnable 接口:
public static void main(String[] arg){
new Thread(run).start();
}
static Runnable run = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(“begin execute”);
try{Thread.sleep(5000);}catch (Exception e){}
System.out.println(“end ”);
}
};
继承与注入同时使用:
public static void main(String[] arg){
new myThread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("456");
}
}).start();
}
static class myThread extends Thread{
public myThread(Runnable run){
super(run);
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(“123");
}
}
输出 123,因为 myThread 中的 run 方法覆盖了父类调用的 run,父类的 run 调用的就是 456 所实现的 run 方法。
2.有返回值的线程
Callable+ Future 方式:
/*
1.Callable规定的执行方法是call
2.call允许抛出异常
3.call有返回值
*/
static Callable call = new Callable() {
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(5000);
return "hello world";
}
};
public static void main(String[] arg)throws Exception {
ExecutorServicepool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Future<String> f = pool.submit(call);
/*
1.向线程池submit后返回Future,通过get方法获取Call的返回值.
2.此处会阻塞
*/
System.out.println("futureGet = "+f.get()); //get方法阻塞
pool.shutdown();
}
Callable+FutureTask 方式:
/*
FutureTask接口实现
RunnableFuture接口,它是
Runnable和Future的结合体
*/
static FutureTask task = new FutureTask(new Callable() {
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(5000);
return "hello world";
}
});
/*
FutureTask的run方法中会执行Call方法。
*/
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
new Thread(task).start();
System.out.println("returnValue = "+task.get());//get阻塞
}
3.停止线程
static Runnable run = new Runnable(){
public void run(){
while (true){
/*
检测到当前线程的interrupt
标识后停止,停止策略需要程
序员设计如何处理
*/
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) break;
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
Thread t = new Thread(run);
t.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
/*设置线程的interrupt标识*/
t.interrupt();
}
强制停止线程(不推荐):
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static Runnable run = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
lock.lock();
try{Thread.sleep(10000);}catch (Exception e){}
lock.unlock();
}
};
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
Thread t = new Thread(run);
t.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
/*强制stop线程,锁未释放,造
成死锁*/
t.stop();
{
lock.lock();
/*永远不会打印*/
System.out.println("get lock");
lock.unlock();
}
}
4.守护线程
线程分为守护线程和非守护线程。如果当前环境中所有 非守护线程 都结束了,那么守护线程也会自动结束。main线程是非守护线程,在main函数中创
建的线程默认是非守护线程。可以通过Thread的setDaemon方法设置线程为守护。
非守护线程:
static Runnable run = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true);
}
};
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
Thread t = new Thread(run);
//Main线程执行完毕后,线程t仍然在执行
t.start();
}
守护线程:
static Runnable run = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true);
}
};
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
/*
线程t设置为守护线程后,随着
main函数的结束,线程t也结束,即使它
还未执行完毕
*/
Thread t = new Thread(run);
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
}
注意:永不停止 线程建议设置为守护线程。 防止线程真正的永不停止,节省 CPU 资源。
5.Object 的 wait、notify、notifyAll 方法进行线程通信
wait、notify、notifyAll 都是 Object 方法,它们都需要结合 synchronized 一起使用。
wait 方法:释放锁,线程进入 wait 状态。
notify 方法:唤醒一个wait状态的线程。
notifyAll:唤醒这个对象锁住的所有线程。
static Object obj = new Object();
static Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "start");
synchronized (obj){
try{obj.wait();}catch (InterruptedExceptione){}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ "end");
}
};
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
new Thread(runnable).start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (obj) {
obj.notify();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("notify"); }
}
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
new Thread(runnable).start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
synchronized (obj){
obj.notifyAll();
System.out.println("notifyAll");
}
}
1.若线程已经被 interrupt,执行 wait 会产生异常。
2.notify 只能从等待队列中的线程唤醒一个,notify 与 wait 应该一一对应。
3.执行 wait 成功后会立刻释放锁,而执行 notify 或notifyAll 后却不会立即释放锁。
6.线程状态
start execute over / stop()
NEW --------------> RUNNABLE -------------------------> TERMINATED
| <------------------------
|sleep(time) |
|wait(time) |
|join(time) |
|LockSupport.parkUntil() |
|LockSupport.parkNanos() |
|--->TIMED_WAITING----------------|
| |
|wait() |
|join() |
|LockSupport.park() |
|--->WAITING----------------------|
| |
|wait for lock to enter |monitor lock acquired
|synchroined lock or method |
|--->BLOCKED----------------------|方便获取更多学习、工作、生活信息请关注本站微信公众号



推荐内容
相关内容
栏目更新
栏目热门
本栏推荐




 湘公网安备 43102202000103号
湘公网安备 43102202000103号