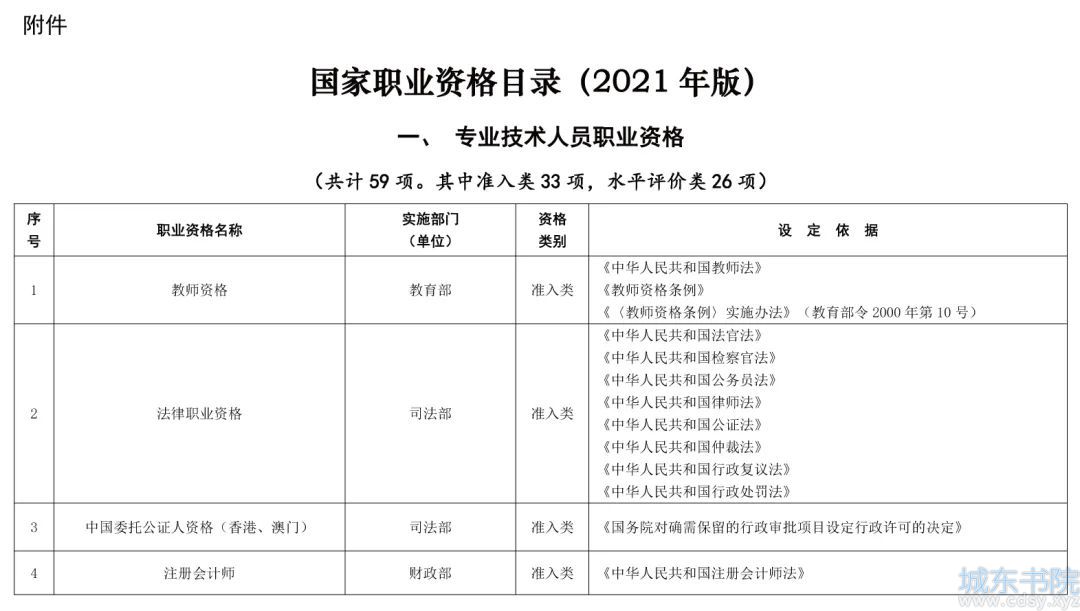
Python 字符串 和 字节串 bytes
1. 字符串
字符串和 repr()
Python不允许直接拼接数值和字符串,程序必须先将数值转换为字符串后才能进项拼接,str()和repr()函数都可以将数值转换为字符串,其中str是Python内置的类型,而repr只是一个函数。此外,repr还有一个功能,它会以Python表达式的形式来表示值。
st = "I will play my fife"
print(st)
print(repr(st)) #输出带引号的字符串,即字符串的Python的表达式形式
>>> I will play my fife
>>> 'I will play my fife'
在交互式解释器中输入一个变量或表达式时Python会自动的使用repr()函数处理该变量或表达式。
长字符串
python 使用三个引号定义长字符串,python还允许使用转义字符(\)对换行符进行转义,转义后的换行符不会“中断‘’字符串。
s = "The quick brown fox \
jumps over the lazy dog" #注意缩进
print(s)
>>> The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog
s = "The quick brown fox \
jumps over the lazy dog"
print(s)
>>> The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog
python 的表达式不允许随便换行,如果程序需要对python表达式进行换行,同样需要使用转义字符(\)进行转义。
num = 20 + 3/4 + \
2*3
print(num)
>>> 26.75
原始字符串
由于字符串中的反斜线\都有特殊的作用,因此当字符串中包含反斜线时就需要对其进行转义,比如写一条Windows的路径:C:\publish\codes\01,在python中是不能直接这样写的,需要写成:C:\\publish\\codes\\01,同时也可以借助原始字符串来解决这个问题。
原始字符串以r开头,原始字符串不会把反斜线当作转义字符,因此可写作:r'C:\publish\codes\01'。
s1 = r'C:\publish\codes\01'
print(s1)
#>>> C:\publish\codes\01
如果原始字符串中包含引号,程序同样需要对引号进行转义,此时用以转义的反斜线会变成字符串的一部分。
s2 = r'"let\'s go", said Charlie'
print(s2)
#>>> "let\'s go", said Charlie
由于原始字符串中的反斜线会对引号进行转义,因此原始字符串的结尾处不能是反斜线,否则字符串结尾处的引号会被转义,导致字符串不能正确结束;
如果字符串结尾需要包含反斜线时,可以改用长字符串写法,或者将反斜线单独写。
"""
打印字符串 Good Morning\
"""
#长字符串写法
s3 = '''Good Morning\\'''
#将反斜线单独写
s4 = r'Good Morning' '\\'
print(s3)
print(s4)
#>>> Good Morning\
#>>> Good Morning\
#区分
s3 = '''Good Morning\''''
print(s3)
#>>> Good Morning'
s3 = '''Good Morning\\'''
print(s3)
#>>> Good Morning\
s3 = 'Good Morning' '\\'
print(s3)
#>>> Good Morning\
s4 = r'Good Morning' '\\'
print(s4)
#>>> Good Morning\
转义字符
| 转义字符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| (在行尾时) | 续行符 |
| \ | 反斜杠符号 |
| \' | 单引号 |
| \" | 双引号 |
| \a | 响铃 |
| \b | 退格 (Backspace) |
| \e | 转义 |
| \000 | 空 |
| \n | 换行 |
| \v | 纵向制表符 |
| \t | 横向制表符 |
| \r | 回车 |
| \f | 换页 |
| \oyy | 八进制数,yy 代表的字符,例如:\o12 代表换行 |
| \xyy | 十六进制数,yy 代表的字符,例如:\x0a 代表换行 |
| \other | 其它的字符以普通格式输出 |
字符串格式化
%- 格式化(不推荐)
>>> name = "hoxis"
>>> age = 18
>>> print("hello, %s. are you %s ?" %(name, age))
hello, hoxis. are you 18 ?
str.format格式化
基本语法是通过{} 和 : 来代替以前的 %。
.format() 函数可以接受不限个参数,位置可以不按顺序。
#不指定参数
>>>"{} {}".format("hello", "world") # 不设置指定位置,按默认顺序
'hello world'
>>> "{0} {1}".format("hello", "world") # 设置指定位置
'hello world'
>>> "{1} {0} {1}".format("hello", "world") # 设置指定位置
'world hello world'
#指定参数
>>> "网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(name=" 城东书院 ", url="www.cdsy.xyz")
'网站名: 城东书院 , 地址 www.cdsy.xyz'
#通过列表设置参数,其中数字0必需
>>> my_list = ['城东书院', 'www.cdsy.xyz']
>>> "网站名:{0[0]}, 地址 {0[1]}".format(my_list)
'网站名:城东书院, 地址 www.cdsy.xyz'
#通过字典设置参数,引用**
>>> site = {"name": " 城东书院 ", "url": "www.cdsy.xyz"}
>>> "网站名:{name}, 地址 {url}".format(**site)
'网站名: 城东书院 , 地址 www.cdsy.xyz'
f-Strings 格式化
f-strings 是指以 f 或 F 开头的字符串,其中以 {} 包含的表达式会进行值替换。
>>> name = 'hoxis'
>>> age = 18
>>> f"hi, {name}, are you {age}?"
'hi, hoxis, are you 18?'
>>> F"hi, {name}, are you {age}?"
'hi, hoxis, are you 18?'
因为 f-strings 是在运行时计算的,那么这就意味着你可以在其中放置任意合法的 Python 表达式,比如:
运算表达式
>>> f"{ 2 * 3 + 1}"
'7'
调用函数
还可以调用函数:
>>> def test(input):
... return input.lower()
...
>>> name = "Hoxis"
>>> f"{test(name)} is handsome."
'hoxis is handsome.'
也可以直接调用内置函数:
>>> f"{name.lower()} is handsome."
'hoxis is handsome.'
在类中使用
>>> class Person:
... def __init__(self,name,age):
... self.name = name
... self.age = age
... def __str__(self):
... return f"{self.name} is {self.age}"
... def __repr__(self):
... return f"{self.name} is {self.age}. HAHA!"
...
>>> hoxis = Person("hoxis",18)
>>> f"{hoxis}"
'hoxis is 18'
>>> f"{hoxis!r}"
'hoxis is 18. HAHA!'
>>> print(hoxis)
hoxis is 18
>>> hoxis
hoxis is 18. HAHA!
多行 f-string
>>> name = 'hoxis'
>>> age = 18
>>> status = 'Python'
>>> message = {
... f'hi {name}.'
... f'you are {age}.'
... f'you are learning {status}.'
... }
>>>
>>> message
{'hi hoxis.you are 18.you are learning Python.'}
这里需要注意,每行都要加上 f 前缀,否则格式化会不起作用:
>>> message = {
... f'hi {name}.'
... 'you are learning {status}.'
... }
>>> message
{'hi hoxis.you are learning {status}.'}
2. 字节串 bytes
字符串str由多个字符组成,以字符为单位进行操作;字节串bytes由多个字节组成,以字节为单位进行操作。
字节bytes对象只负责以字节(二进制格式)序列来记录数据,采用合适的字符集,字符串与字节串可以互换。
字符串转换为bytes对象:
- 如果字符串都是ASCII字符,通过在字符串前加b来构建字节串值;
- 调用bytes()函数,并指定字符集;
- 调用字符串本身的.encode()(编码)方法,并指定字符集,解码用.decode()。
#创建一个空的bytes
b1 = bytes()
b2 = b''
>>> b1 = bytes()
>>> b1
b''
>>> b2 = b''
>>> b2
b''
>>> b3 = 'hello'
>>> bytes(b3 , encoding = 'utf-8') #指定编码(字符集)
b'hello'
>>> b4 = '你好'
>>> bytes(b4 , encoding = 'utf-8')
b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd'
>>> b5 = '我是'
>>> b6 = b5.encode('utf-8')
>>> b6
b'\xe6\x88\x91\xe6\x98\xaf'
>>> b7 = b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd'
>>> b8 = b7.decode('utf-8') #解码
>>> b8
'你好'





 湘公网安备 43102202000103号
湘公网安备 43102202000103号