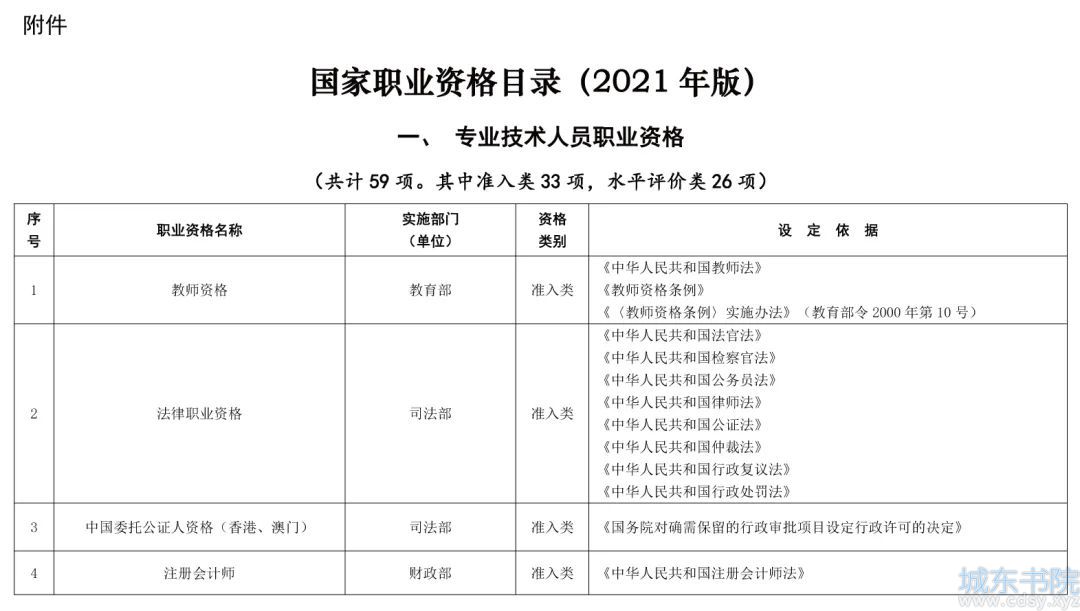
Python 多线程测试总结
时间:12-14来源:作者:点击数:
目的
- 验证 Python 解释器创建的线程是否是 伪并行,实验一验证。
- 验证 Python 解释器能创建最大线程数,实验二验证。
背景知识
- Python(这里说的是 C Python)支持多线程,而且 Python 的一个线程也确实对应一个真正的操作系统线程。不过 Python 里面有个全局锁(GIL:Global Interpreter Lock),正是这个GIL限制了 Python 的多线程并发能力。
- Python 难以实现用户级的线程库和复杂递归应用,一旦超越这个限制, 程序就会崩溃。
实验一
测试场景
1、使用单线做连续两次 CPU 序列计算,统计计算时间,模拟单线程 CPU 计算密集型业务。
测试脚本:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import threading
import time
start = time.time()
def count(n):
while n > 0:
n -= 1
print "start serial"
count(100000000)
count(100000000)
print "serial Elapsed Time: %s" % (time.time() - start)
print "start Para"
start = time.time()
t1 = threading.Thread(target=count,args=(100000000,))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=count,args=(100000000,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print "Para Elapsed Time: %s" % (time.time() - start)
统计时间为:10.5480000973s
2、使用多线程并行两次 CPU 计算,统计计算时间,模拟多线程CPU计算密集型业务。
测试脚本:同上 统计时间:51.0369999409s
3、使用单线程Python下载5个web页面,统计时间,模拟单线程IO处理密集型业务。
测试脚本:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import urllib2
import time
hosts = ["http://yahoo.com", "http://google.com", "http://amazon.com",
"http://ibm.com", "http://apple.com"]
start = time.time()
#grabs urls of hosts and prints first 1024 bytes of page
for host in hosts:
url = urllib2.urlopen(host)
print url.read(50)
print "Elapsed Time: %s" % (time.time() - start)
统计时间:约 35.5 s
4、使用5个线程并行下载同样的5个web页面,统计时间,模拟多线程IO处理密集型
测试脚本:
#!/usr/bin/env python
import Queue
import threading
import urllib2
import time
import stackless
hosts = ["http://yahoo.com", "http://google.com", "http://amazon.com",
"http://ibm.com", "http://apple.com"]
queue = Queue.Queue()
class ThreadUrl(threading.Thread):
"""Threaded Url Grab"""
def __init__(self, queue):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.queue = queue
def run(self):
while True:
#grabs host from queue
host = self.queue.get()
#grabs urls of hosts and prints first 1024 bytes of page
url = urllib2.urlopen(host)
print url.read(50)
#signals to queue job is done
self.queue.task_done()
start = time.time()
def main():
#spawn a pool of threads, and pass them queue instance
for i in range(5):
t = ThreadUrl(queue)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.start()
#populate queue with data
for host in hosts:
queue.put(host)
#wait on the queue until everything has been processed
queue.join()
main()
print "Elapsed Time: %s" % (time.time() - start)
统计时间:约9.3 s
结论一
- 对于CPU密集型的程序,顺序执行比并发执行效率更高,这是因为并发时GIL带来了额外的开销。
- 对于IO密集型的程序,Python的多线程并发执行还是能够提高效率的,因为,Python线程在等待IO时,会释放GIL;
- xCloud性能测试业务脚本是以IO处理为主,CPU计算为辅,初步判断采用Python多线程并发是能够提高测试性能的。
实验二
测试场景
1、使用hackysack游戏程序,该程序属于只有简单的CPU计算,所以模拟Python所能创建的线程最大数。其他程序能够创建的线程数只能比该程序更少。
测试脚本:
import thread
import random
import sys
import Queue
class hackysacker:
counter = 0
def __init__(self,name,circle):
self.name = name
self.circle = circle
circle.append(self)
self.messageQueue = Queue.Queue()
thread.start_new_thread(self.messageLoop,())
def incrementCounter(self):
hackysacker.counter += 1
if hackysacker.counter >= turns:
while self.circle:
hs = self.circle.pop()
if hs is not self:
hs.messageQueue.put('exit')
sys.exit()
def messageLoop(self):
while 1:
message = self.messageQueue.get()
if message == "exit":
debugPrint("%s is going home" % self.name)
sys.exit()
debugPrint("%s got hackeysack from %s" % (self.name, message.name))
kickTo = self.circle[random.randint(0,len(self.circle)-1)]
debugPrint("%s kicking hackeysack to %s" % (self.name, kickTo.name))
self.incrementCounter()
kickTo.messageQueue.put(self)
def debugPrint(x):
if debug:
print x
debug=1
hackysackers=5
turns = 5
def runit(hs=10,ts=1000,dbg=1):
global hackysackers,turns,debug
hackysackers = hs
turns = ts
debug = dbg
hackysacker.counter= 0
circle = []
one = hackysacker('1',circle)
for i in range(hackysackers):
hackysacker(`i`,circle)
one.messageQueue.put(one)
try:
while circle:
pass
except:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
#runit(dbg=1)
runit(1000,1000,0)
测试结果:从1100个线程左右开始报错:无法创建新线程
2、并发下载 web 页面,不断增加并发用户,直到并发出错。
结论二
- 对于 CPU 密集型的程序,Python 所能创建最大线程数在1000左右。
- 因为无测试数据,对于IO密集型的程序,初步推测,Python 的多线程并发数不可能超过 1000。
- xCloud 性能测试业务脚本是以IO处理为主,CPU 计算为辅,处理程序比实验中程序复杂,初步判断
采用标准Python多线程并发,单进程并发用户数很难超过 1000。
问题
本次下载 web 页面测试采用的是 Python 标准库函数,单页面下载耗时9秒以上,这个速度不可容忍,如采用 Python 脚本,使用C或其它语言编译型语言扩展数据收发包模块势在必行。
方便获取更多学习、工作、生活信息请关注本站微信公众号



上一篇:Python 统一返回对象
下一篇:Python 实现文件 FTP 上传下载




 湘公网安备 43102202000103号
湘公网安备 43102202000103号